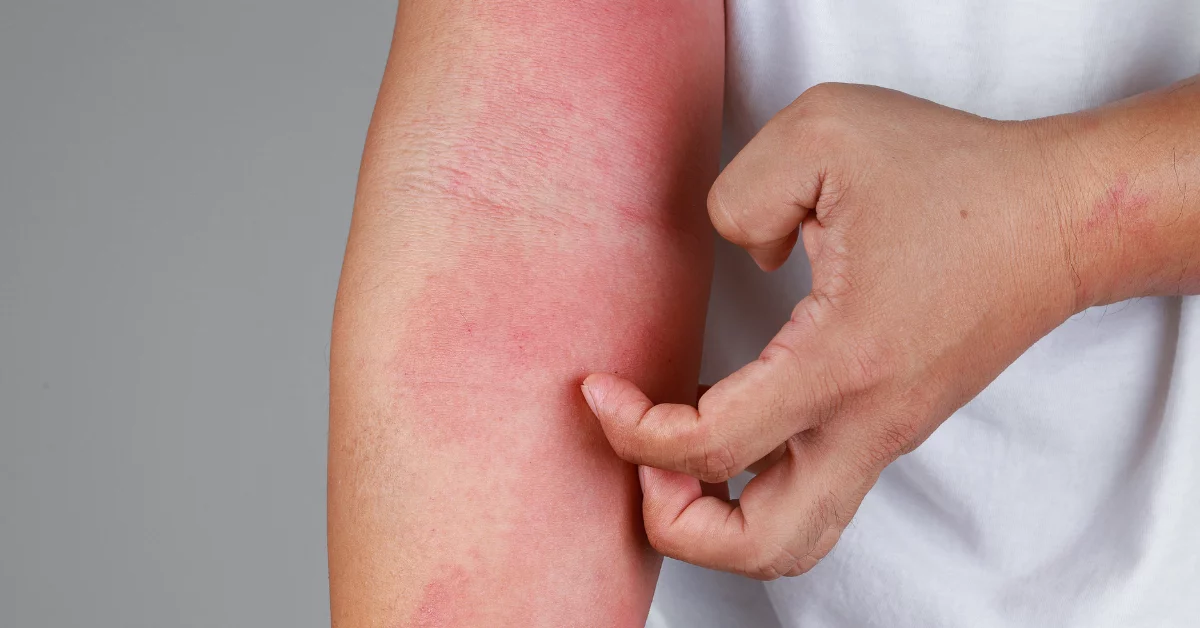
Eczema is a condition which can cause inflamed, itchy, dry skin, as well as the appearance of rashes, scaly patches, blistering, and/or discoloration on the surface of the skin. Eczema is rather common, affecting over 30 million Americans. It can be mild or severe and may appear at any age although it is most common among children and adolescents. In many cases, eczema is a chronic condition which will flare up periodically.
Types of eczema include:
- Atopic Dermatitis: This is the most common form of eczema. It typically affects children and fades as they grow into adulthood. This condition is often experienced by people who also have asthma and hay fever.
- Contact Dermatitis: Skin redness and irritation may be the result of an allergic reaction. Substances which can cause an outbreak of contact dermatitis vary from person to person, and can include skin creams, certain metals in jewelry, cleaning products, or latex.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: This type of eczema, also known as pompholyx, causes blisters to develop on the fingers, palms of your hands, and sometimes the soles of your feet. It can be caused by allergic reactions, stress, or fungal infection of the affected area.
- Hand & Foot Eczema: In some cases eczema will only appear on the hands or feet, usually due to allergic reactions or infections. This can overlap with other types of eczema and can be rooted in atopic or contact dermatitis.
- Neurodermatitis: A condition which causes thick, scaly patches to form on the skin. Neurodermatitis can cause severe itching and the risk of infection if the scaly patches are opened by scratching. It often begins as another form of eczema or as the skin disease psoriasis.
- Stasis Dermatitis: When you have circulation issues due to weakened veins in your legs, fluid can leak into the skin, causing pooled blood and varicose veins which may be covered with red, scaly skin. This serious issue can cause swelling and aching in your lower legs.
- Nummular Eczema: This form of eczema differs most in appearance from the other types of eczema, causing small, round patches to form on the skin. It may be an immune reaction to an allergen or insect bite, or in rare cases from dry skin. Nummular eczema is most likely to affect people who already have another form of eczema.
Eczema can result from a range of causes, which will differ from person to person. Genetics are often a factor, with some people having skin which is not able to properly retain enough moisture to stay healthy. While eczema is not contagious, there are also environmental factors which can come into play. Many forms of eczema can be triggered by allergic reactions or immune responses, and stress can also play an important role in causing eczema flare-ups. Eczema is also most likely to occur if you live in a very dry climate or have a job where you are frequently exposed to irritating chemicals.
There may be a wide diversity of symptoms depending on the type and severity of the issue. Some of the most common signs of eczema include dry skin, scaly patches, and/or rashes which cause redness, itching, irritation, and inflammation. Eczema can appear anywhere on the surface of the skin, but most commonly emerges on the neck, hands and feet, and creases or folds in the skin such as at the elbows and knees. If skin becomes very dry, it may crack and bleed.
The causes of eczema cannot always be definitively identified, but there are a variety of factors that may place you at a higher risk. Genetics can be an important contributor, as you are more likely to develop many types of eczema if you have a family history of the condition. Eczema can also be triggered by environmental factors, and you are also at a higher risk if you have allergies or live in a cold, dry climate. Outbreaks can also be more likely if you are under severe emotional stress.
A dermatologist can usually diagnose eczema by performing a physical examination of the skin. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be required, in which a small amount of skin is removed for testing to determine the precise cause of the rash.
Treatments for eczema will depend on the nature and cause of the issue, by may include moisturizing skin creams, topical corticosteroids, or creams or ointments which modulate your body’s immune response. You may be told to avoid certain irritants or allergens if they are contributing to the issue. Phototherapy, also known as light therapy, may also be useful for eczema rashes which do not respond to topical treatments. In severe cases, systemic immunologics or biologics may be necessary to mediate the immune response which causes eczema flare-ups.
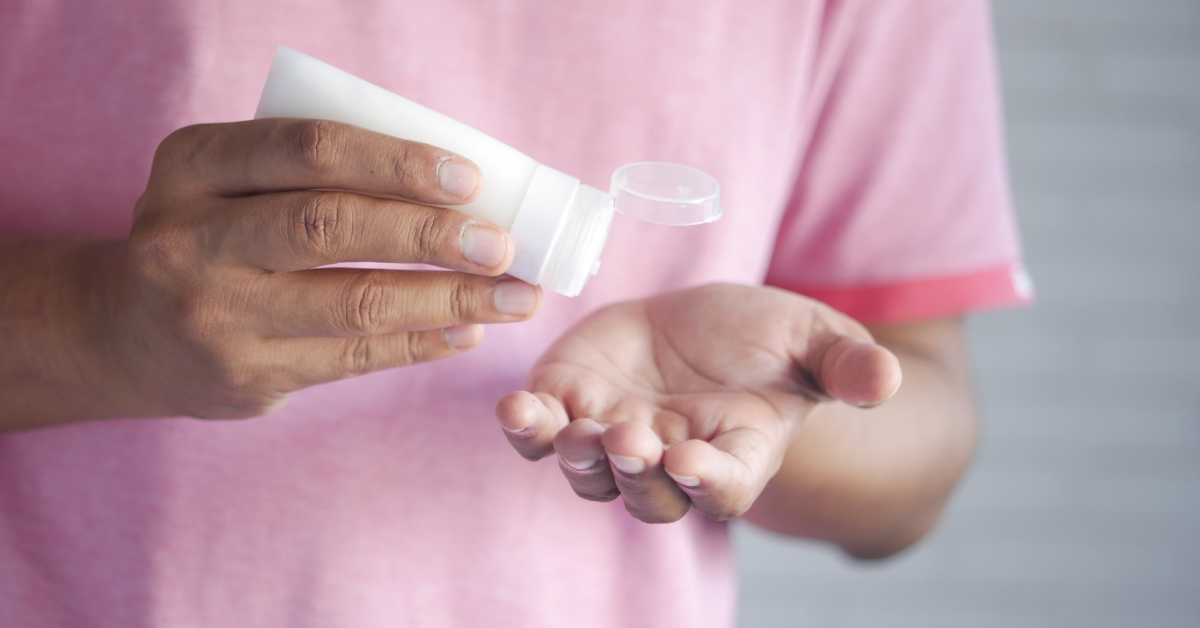

Not all of the causes of eczema can be avoided, but useful preventive measures include moisturizing regularly, shortening baths and showers, and avoiding any known chemical or allergy triggers. It may also be helpful to maintain a healthy diet and get regular exercise. You should also try to avoid scratching rashes to avoid infection and other complications.
If left untreated, eczema can cause chronic itching, redness, inflammation, and irritation, which beyond being uncomfortable and unsightly could lead to a higher risk of infection from scratching or cracking of the skin. You should contact a dermatologist if your eczema is causing difficulty sleeping or getting through the day comfortably, or if you notice red streaks, pus, or other signs of infection.
Atopic and contact dermatitis can both be related to most of the other types of eczema, and the condition can also be secondary to psoriasis in some cases.




