Skin cancer is curable if detected and treated early. The main site of the tumor determines the skin cancer subtype. Basal cell skin cancer develops in the skin’s own cells. Melanoma is a kind of skin cancer that affects melanin-producing cells. In this article, you will learn about the most common types of skin cancer, how they appear, and who is most at risk of acquiring them.
What types of skin cancer should I look out for?
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
- The major risk factor for basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is prolonged sun exposure. Sun exposure is an element of it, especially for fair-skinned people who get sunburned easily.
- In comparison to those with darker skin tones, individuals with a lighter complexion, lighter eyes, and redder or blond hair are more likely to develop basal cell carcinoma (BCC).
- BCC tends to manifest in the elderly, usually beyond the age of 50, although it may happen to anybody at any age; males have a slightly higher risk than women.
- Round, flesh-colored growths, pearl-like bumps, or pinkish patches of skin are common appearances of basal cell carcinomas (BCCs).
- Although BCCs most often appear on the arms, neck, and head, they are capable of developing on any part of the body, including the legs, chest, and stomach.
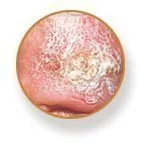
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
- Similar to BCC, prolonged sun exposure is the main cause of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
- SCC is more common in people with lighter skin tones, lighter eyes, and lighter hair colors (blond or red) than in those with darker skin tones.
- Common symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma include a red, hard lump, a scaly area, or a recurrent sore.
- Sunken cysts (SCCs) often develop on areas of skin that are constantly exposed to the sun, including the back, arms, neck, face, and ear lobes.
- Deep skin growth is a risk for SCC, which may lead to deformity and skin damage.
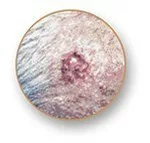
Melanoma
- Many refer to melanoma as “the most serious skin cancer” because of its propensity to metastasize.
- Melanoma may occur in two ways: first, as an existing mole, or second, as an unusually dark area on the skin.
- Early detection of melanoma may be facilitated by familiarity with the ABCDE warning indicators.
- The most important thing is to find problems early and fix them quickly.
Do these cancers have any warning indicators?
Precancerous skin growths known as actinic keratoses (AKs) have the potential to progress into squamous cell carcinoma, a prevalent form of skin cancer. The lack of sun protection measures, such as sunscreen, clothes, and shade, makes these precancerous skin growths prevalent. Actinic keratoses are scaly lumps that are often seen on the face and scalp and are frequently seen in elderly men who are bald.
Because of the sun’s damaging rays, your skin might be damaged if you do not use sun protection. Even though your body may be able to heal some of this damage, the sun’s rays will continue to cause harm to skin that is not covered. Over the course of your lifetime, this damage accumulates and has the potential to create precancerous alterations in your skin.
Checking the skin on a regular basis and taking precautions against the sun are essential for early identification and prevention.